| ENZYMES |
USAGE |
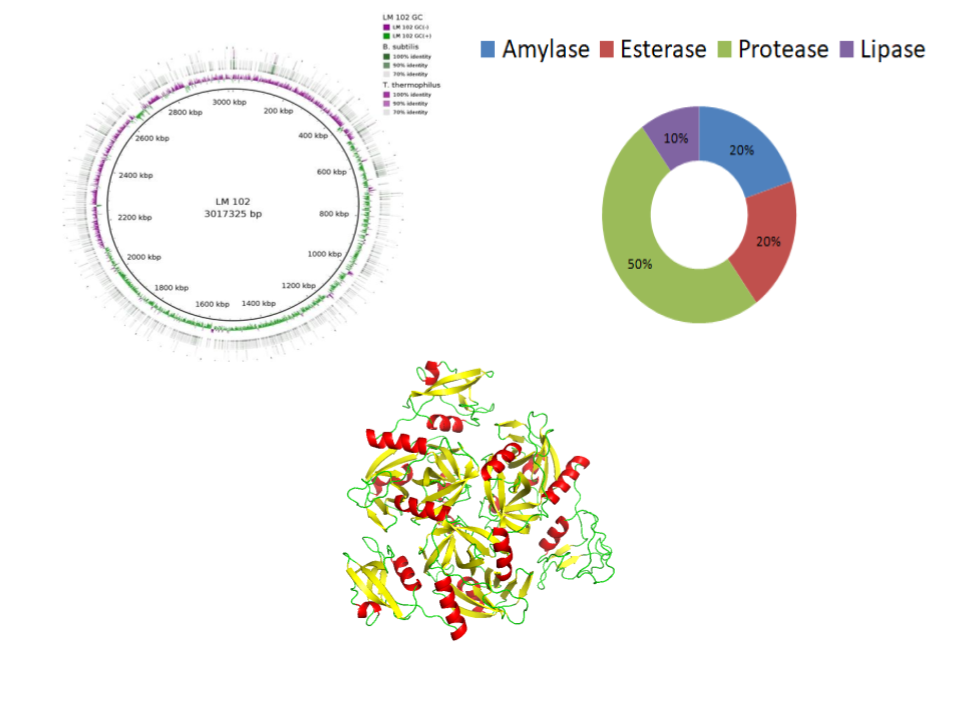
| Lipase: Lipase acts on triacylglycerols and releases fatty acids. Determination of its activity is calculated by titration of free fatty acids. Lipase can be classified into three different classes based on its positional and fatty acid specificity. Most of the lipases belong to sn-1,3 specific lipase. These lipases hydrolyse/esterify fatty acid specifically at the either/both sn-1 and sn-3 position.
| food processing, detergent, pharmaceutical, leather, textile, cosmetic, and paper industries |
| Amylase: Amylase can be classified into three types: alpha-amylase, beta-amylase, and gamma-amylase. The three types differ in how they hydrolyze the polysaccharide bonds.
| food processing, textile, paper and detergent |
| Esterase: An esterase is a hydrolase enzyme that splits esters into an acid and an alcohol in a chemical reaction with water called hydrolysis. A wide range of different esterases exist that differ in their substrate specificity, their protein structure, and their biological function.
| food processing, alcoholic beverages, degradation of natural materials and industrial pollutants |
| Protease: On the basis of the site of the peptide bond cleavage, proteolytic enzymes are divided into two broad groups; Exopeptidase & Endopeptidase
| food processing, pharmaceuticals, leather, silk, bakery, soy, meat and breweries |